Tlatilco pottery and its influence in Mesoamerica
Tlatilco pottery, originating from the archaeological site of the same name located in the present-day Valley of Mexico, stands out for its sophistication and diversity, reflecting the deep cultural roots of its creators from the Early Formative period (c. 1200-900 B.C.).
With a wealth of forms ranging from detailed human figures to animal-shaped vessels and innovative designs, this pottery is not only a testament to the artistic virtuosity of Tlatilco, but also to the complex network of cultural interactions, especially with the Olmec culture.
Discover how these age-old creations continue to fascinate experts and aficionados alike, inviting us to explore the stories and mysteries they hide.

Origins and geographic context of Tlatilco pottery
The archaeological site of Tlatilco, whose name comes from the Nahuatl word meaning “place of hidden things”, is located in the heart of the Valley of Mexico, near what is now Mexico City.
This pre-Columbian enclave flourished during the Early Formative period, around 1200 to 900 B.C., and is famous for being one of the first settlements with a complex and distinctive culture in Mesoamerica. The Tlatilco area benefited from a privileged geographical location, with access to abundant natural resources and a strategic position that facilitated interactions with other Mesoamerican regions.
The topography of the Valley of Mexico, characterized by its vast plains surrounded by mountains and volcanoes, created a fertile environment conducive to the development of agricultural communities. Nearby rivers and lakes provided not only a constant supply of water but also avenues for trade and communication with other Mesoamerican cultures.
This geographical context not only sustained the daily life of the inhabitants of Tlatilco, but also influenced their religious practices and rituals, as well as their art and crafts, especially ceramics.
Where was each pre-Columbian culture?
Check our interactive map to see its period and location.
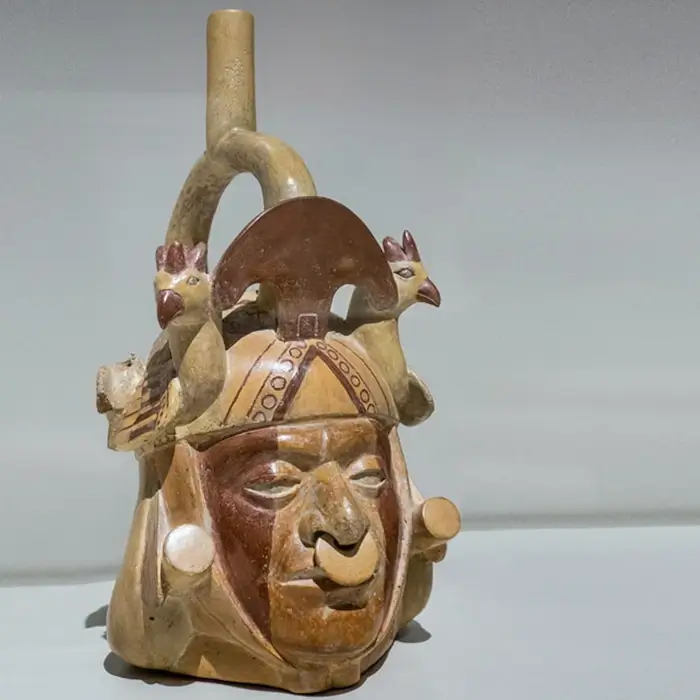
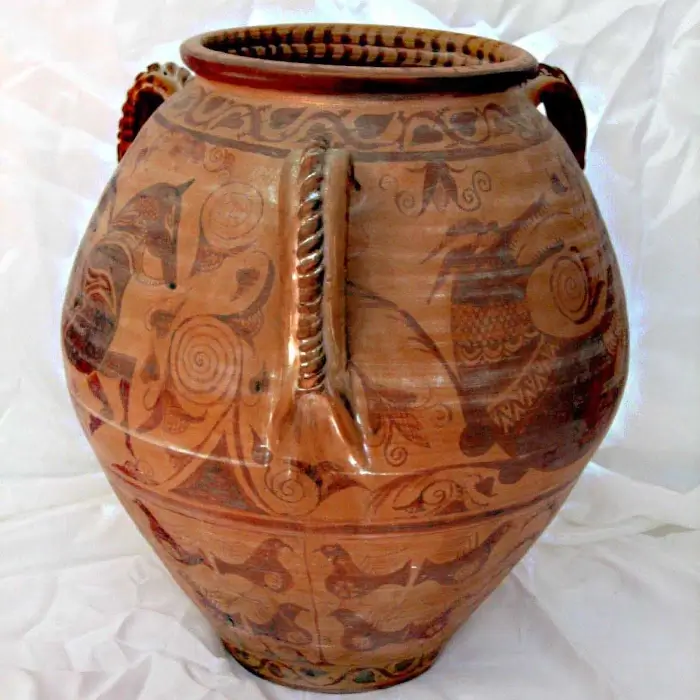
The pottery of Tlatilco is particularly notable for its diversity and sophistication, reflecting the rich cultural tapestry of this archaeological site. Tlatilco potters mastered a wide range of techniques and styles, producing everything from detailed human figures to vessels with animal shapes and geometric designs.
The study of Tlatilco ceramics, along with other archaeological finds, suggests that this community was well integrated into the broader commercial and cultural network of Mesoamerica. Exchanges with distant regions allowed the Tlatilcans to access exotic materials and share artistic and technological ideas, which further enriched their own ceramic production. This interaction with diverse Mesoamerican cultures and ceramics would lay the foundation for the development of distinctive characteristics in Tlatilco pottery, a topic we will explore later in the article.
Main characteristics of Tlatilco ceramics
Tlatilco pottery is an exceptional testimony to the creativity and skill of the artisans of one of the most enigmatic pre-Columbian cultures of Mesoamerica. This pottery not only served a functional purpose, but also stood as a channel of artistic and symbolic expression, reflecting the beliefs and worldview of the Tlatilco society.
It is remarkable the detail with which Tlatilco potters depicted human figures, which often showed detailed features and unique facial expressions, indicative of a deep interest in individuality and the human condition.
In addition, Tlatilcan ceramics are notable for their use of fine incised lines and color applications, which not only added beauty to the objects, but also had symbolic meanings. The colors used in the decoration of these pieces were often derived from natural materials available in the region, demonstrating a deep knowledge of their natural environment.
Duality is another recurring theme in Tlatilco ceramics, reflected in the representation of figures with two faces or in the symmetry of their designs. This characteristic could be linked to the worldview of the inhabitants of Tlatilco, where duality and balance between opposites were fundamental principles of their cosmovision.
Analysis of manufacturing techniques reveals that Tlatilco artisans mastered a variety of techniques, including hand modeling and the use of molds, which allowed them to produce a wide range of shapes and sizes. This versatility is evidence of a sophisticated understanding of the properties of ceramic materials and a high degree of craft specialization.
Exploring cultural influences on Tlatilco pottery in subsequent sections will highlight how this artifact not only reflected local traditions, but also incorporated elements of contemporary and earlier cultures, demonstrating the complexity of cultural interactions in pre-Columbian Mesoamerica.
Cultural influences in Tlatilco ceramics
The ceramic pieces of Tlatilco not only reflect the technical virtuosity of its artisans, but also a rich cultural exchange that characterized this Mesoamerican region. These objects are imbued with external influences, particularly from the Olmec culture, considered by many as the “mother culture” of Mesoamerica. The presence of Olmec iconography and artistic styles in Tlatilca ceramics suggests a dynamic interaction between these cultures, possibly through trade or the dissemination of religious beliefs and ceremonial practices.
In addition, the elaboration of Tlatilco figurines, often depicting female figures with intricate detail and vivid poses, reflects not only technical mastery but also the importance of the female figure in Tlatilco society. This emphasis on the representation of femininity and, at times, duality, as seen in the two-headed figures, may have roots in the religious beliefs and worldviews shared between Tlatilco and other Mesoamerican cultures of the time.
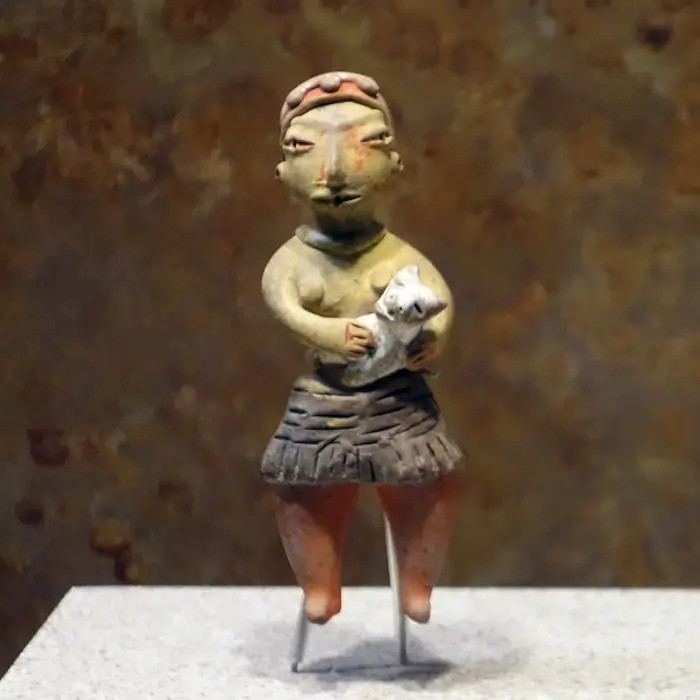

Tlatilco’s proximity to natural resources, such as lakes and rivers, is reflected in the subject matter of some of its ceramic pieces, which often include depictions of aquatic animals and birds. This focus on local nature not only highlights the symbiotic relationship between the community and its environment, but also suggests a fusion of cultural influences that valued the representation of nature in art.
It is clear that Tlatilco ceramics were much more than utilitarian or decorative objects; they were expressions of a complex society that was in constant dialogue with its cultural neighbors. As we explore the most representative pieces of Tlatilco pottery in the following sections, we will see how these influences manifest themselves in specific works, and how these artifacts continue to provide an invaluable window into the cultural interconnections of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica.
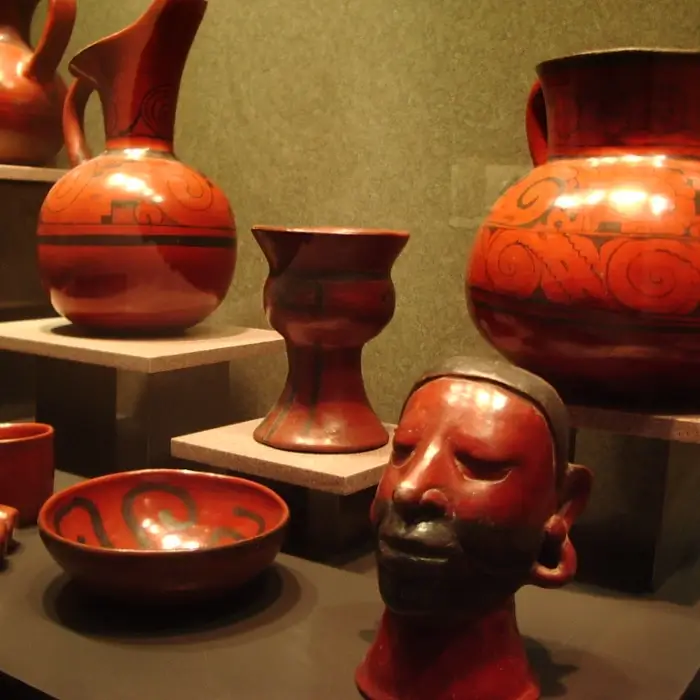
The most representative ceramic pieces from Tlatilco
Tlatilco pottery is an artistic expression that reflects the complexity and richness of this pre-Hispanic culture settled in the Valley of Mexico. Among its most outstanding pieces are figurines, vessels and seals, each with distinctive characteristics that reveal important aspects about their beliefs, daily practices and interaction with other cultures of Mesoamerica.
Tlatilco figurines are particularly notable for their detailed depiction of human forms, many of which are notable for their postures, ornamentation and expression of emotion. These pieces serve not only as a testament to the craftsmanship of Tlatilco’s potters but also as a window into the gender roles, social status, and spirituality of the period.
As for the vessels, they are distinguished by their variety of shapes and sizes, from vessels to bowls and plates, many of which are decorated with geometric motifs or representations of local flora and fauna. These decorative elements not only embellish the pieces but could also have symbolic or ritual meanings, an aspect that links to the cultural and ceremonial practices of Tlatilco.
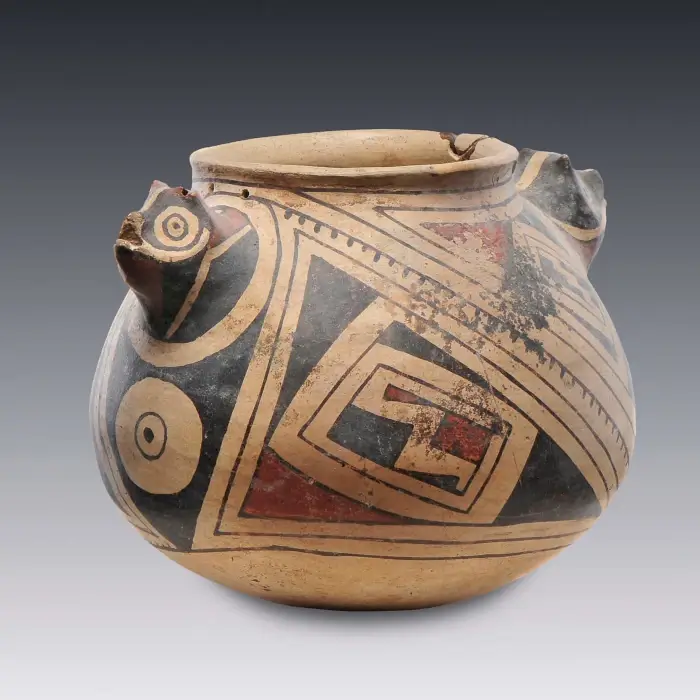

Buy pre-Columbian ceramics
Find original pieces and also reproductions identical to the traditional ceramic works that were made in pre-Columbian America and that are only found in museums, making them affordable.
Ceramic stamps, although less frequent, constitute another important facet of Tlatilco pottery. Used to imprint designs on other surfaces, these stamps reveal a repertoire of artistic and symbolic motifs that suggest the existence of a complex iconography and possibly communication or recording systems.
The exploration of these emblematic pieces prepares us to appreciate the archaeological and cultural importance of Tlatilco ceramics in the next segment, where we will delve into how these objects found in archaeological finds contribute to our understanding of ancient Mesoamerican societies and their invaluable legacy to history and culture.
Archaeological and cultural significance of Tlatilca pottery
Tlatilco ceramics represent a crucial component for the understanding of the formative cultures of Mesoamerica. These pieces, handmade without the use of molds, show a mastery and attention to detail that reflect the complex society of which they were a part. The figurines from Tlatilco, often representing female figures with elaborate hairstyles and vivid expressions, stand out for their artistic value and their reflection of the importance of the female figure in society.
These archaeological pieces, found in burials and ritual contexts, provide valuable information on the funerary practices, religious beliefs and social structure of Tlatilco. In addition, the iconography present in some pieces suggests influences from contemporary and earlier cultures, such as the Olmec, indicating a significant network of cultural exchange and interaction in the region.
The investigation of the archaeological contexts of Tlatilco figurines is fundamental to understanding their use and meaning within their society. The detailed study of pieces from secure contexts allows a deeper understanding of the cultural and ceremonial practices of this central formative culture of Mesoamerica.
In short, Tlatilco ceramics are valuable not only for their aesthetics and technique, but also for the light they shed on the daily life, beliefs, and interactions of Mesoamerican cultures. This clay legacy continues to be an invaluable source of knowledge for archaeologists and scholars, allowing for a greater understanding of the complex cultural networks of ancient Mesoamerica.





