The secrets of Olmec pottery: Keys to their culture.
Olmec pottery, an artistic manifestation of the first great Mesoamerican civilization, shows us the essence of a culture that laid the foundations for future developments in the region.
The Olmec artisans, skilled in the handling of clay, created everything from portable figures to monumental stone heads, each reflecting both everyday and mythological aspects of their society.
This art, especially jade and ceramic sculptures, served not only as an aesthetic expression but also as a means of expressing religious beliefs and ritual practices.
To discover Olmec pottery is to enter a world where the divine and the earthly intertwine, revealing a complexity and sophistication that many consider ahead of its time. I invite you to explore the mysteries of a civilization that, although disappeared, continues to surprise us with each piece that comes to us.
- Learn about Olmec Ceramics
- The Importance in the history of Olmec Ceramics
- Characteristics of Olmec Ceramics
- Iconography and Symbolism in Olmec Art
- How the Olmecs Made Pottery
- Functions and Uses of Olmec Ceramics
- Significant Archaeological Finds in the Olmec Culture
- Influence of Olmec Art and Ceramics in Mesoamerica
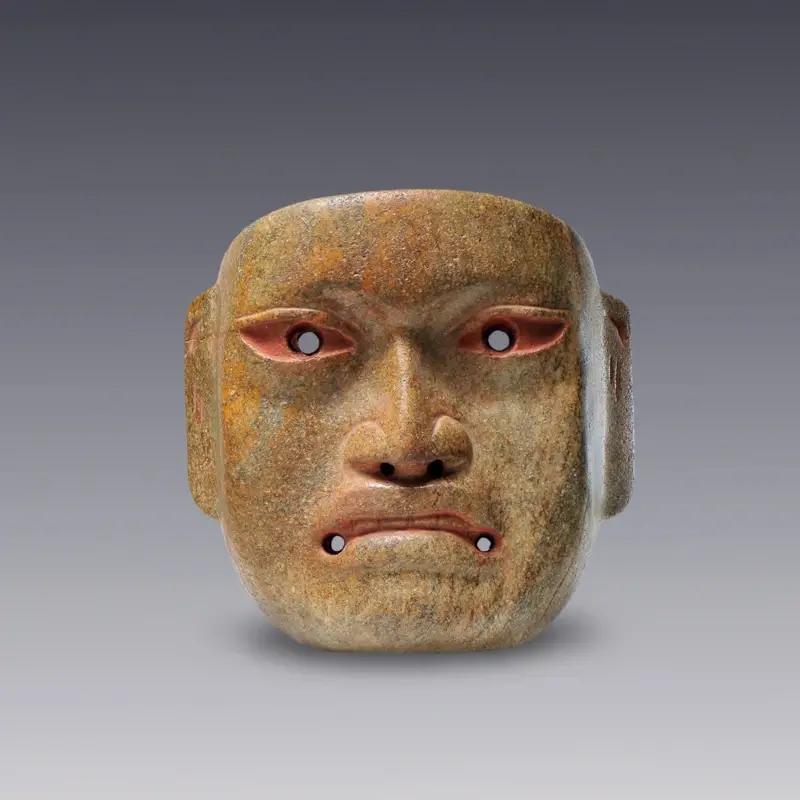

Learn about Olmec Ceramics
The Olmec civilization, known as the first great civilization of Mesoamerica, was established in the tropical lowlands of the present-day Mexican states of Veracruz and Tabasco. This initial development occurred in Soconusco, and over time, the Olmec civilization expanded throughout these regions characterized by their swampy lowlands, interrupted by low hills, ridges and volcanoes.
Significant sites such as San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán and La Venta became the centers of activity for this culture. San Lorenzo, located some 35 miles south of the Gulf of Mexico, and La Venta, further east and near the Gulf coast in Tabasco, were epicenters of their cultural flourishing between 1200 and 400 B.C., where they stood out for their diet based initially on fishing and hunting, later incorporating corn and other crops.
The Olmec are especially remembered for their colossal stone heads, which are considered among the most striking works of art in ancient America. These heads, carved from basalt and with unique facial features, are believed to be portraits of Olmec rulers, often showing the subject wearing protective helmets, indicating their political and religious importance.
In addition to their impressive art, the Olmec bequeathed cultural and religious foundations to later Mesoamerican civilizations and are considered the “mother culture” of the region. Their practices included the Mesoamerican ball game and possibly ritual bloodletting, elements common to subsequent Mesoamerican societies. The impact of the Olmec civilization extended far beyond its urban centers, influencing the development of other important cultures such as the Maya, Zapotec and Teotihuacan.
Where was each pre-Columbian culture?
Check our interactive map to see its period and location.
The richness and complexity of Olmec ceramics, which we will explore in later sections, not only reflect the artistic mastery of this civilization, but also its profound cultural and spiritual significance. Through clay and mud, the Olmecs captured their cosmovision, creating pieces that are a testimony of their connection with nature and the divine, and that today continue to fascinate both experts and admirers of pre-Columbian art.
The Importance in the history of Olmec Ceramics
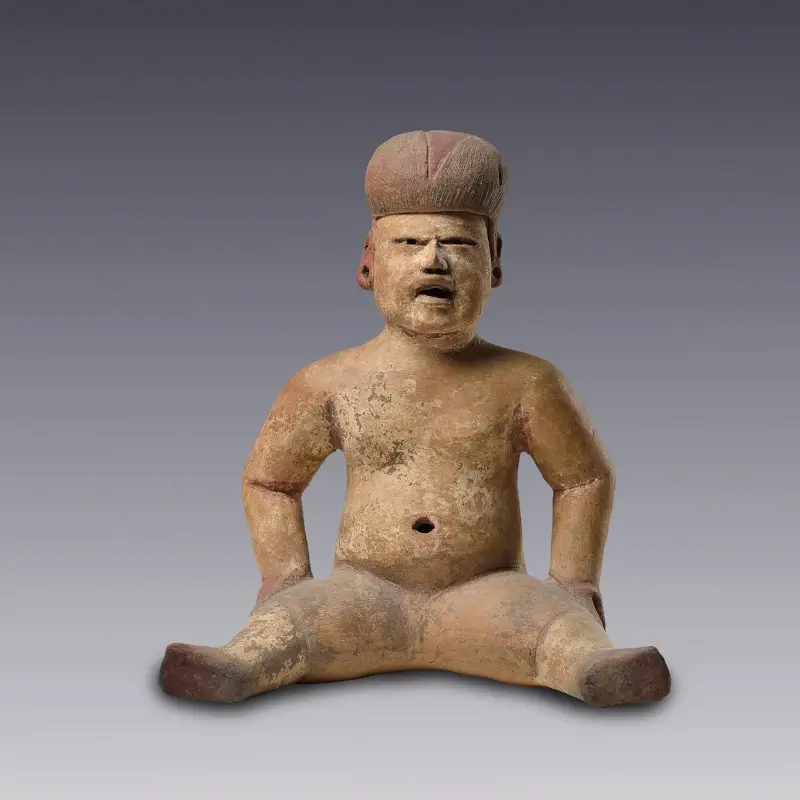
Olmec pottery, renowned for its elaborate iconography and sophisticated technique, occupies a preeminent place in the Mesoamerican context, serving as a cornerstone for understanding the cultural and artistic practices of the region’s ancient civilizations. The Olmec, considered the “mother culture” of Mesoamerica, left an artistic legacy that includes both monumental stone heads and detailed ceramic figures, reflecting the complexity of their spiritual beliefs and social structure.
Olmec ceramic figurines, known for their elongated features and enigmatic smiles, not only demonstrate the technical mastery of their creators, but also invite reflection on the mystical realms that permeated ancient Mesoamerican society. These pieces not only capture the imagination, but also deepen our understanding of this enigmatic civilization, highlighting the importance of agriculture and ritual practices through their depictions of deities such as the Corn God and mythological figures such as the celestial dragon.

Museo Amparo
Olmec art not only influenced contemporary Mesoamerican cultures, but also laid the foundation for later civilizations, such as the Maya and Aztecs, who inherited and adapted their iconography and religious practices. This artistic legacy, especially evident in ceramics, highlights the centrality of the Olmecs in the cultural and artistic development of Mesoamerica, underscoring their innovative role in the region’s history.
Characteristics of Olmec Ceramics
Olmec pottery, a reflection of the ingenuity and spirituality of this precursor culture of Mesoamerica, stands out for its stylistic diversity and the mastery of its techniques and materials. The Olmec explored a wide range of forms, from humanoid figures to vessels and other containers, each loaded with meaning and purpose. Technical skill is revealed in the use of different types of clay and in the meticulous modeling process, where attention to detail and precision were paramount.
The styles vary from the naturalistic representation of figures and animals, highlighting jaguars and eagles, to more abstract and symbolic forms, such as the iconic “man-jaguar”. The latter, possibly considered a supreme deity, illustrates the fusion of human and feline characteristics, reflecting the Olmec cosmovision and its connection with the divine and the earthly. The use of colors and the application of pigments complemented these works, adding an additional dimension to their visual and symbolic richness.

Buy pre-Columbian ceramics
Find original pieces and also reproductions identical to the traditional ceramic works that were made in pre-Columbian America and that are only found in museums, making them affordable.
Olmec pottery not only served as an object of daily or ritual use, but also as a means to document and transmit the beliefs, myths and social structures of their time. Through this artistic expression, the Olmec managed to leave an indelible mark on the cultural fabric of Mesoamerica, influencing later civilizations and allowing us, even today, to peer into the depths of their legacy.
Iconography and Symbolism in Olmec Art
The iconography and symbolism in Olmec ceramics are a vivid reflection of the worldview and spiritual richness of this ancient civilization.
Through their clay creations, the Olmecs depicted not only human figures and deities, but also a wide range of animals, such as jaguars, eagles and snakes, which occupied a prominent place in their mythological pantheon. These figures not only served as artistic representations, but also embodied divine powers and attributes, integrating the natural with the supernatural.
Among the most emblematic deities is the figure of the “man-jaguar” mentioned above, a hybrid being between human and jaguar that symbolizes the fusion between the spiritual and the earthly world, and possibly represented the supreme being in the Olmec religion.
In addition, the Olmec assigned special significance to certain animals in their environment, identifying them with divine beings and believing that powerful rulers could transform themselves at will into these fearsome creatures.
Everyday scenes also had their place in Olmec ceramics, where daily activities and rituals were depicted, thus offering a window into the life and customs of this culture. These representations, along with the more sacred iconography, provide a deeper understanding of Olmec society, showing the interconnection between their daily life, their natural environment and their rich spiritual sphere.
How the Olmecs Made Pottery
One of the characteristics of Olmec ceramics was that they presented excised designs in many of their pieces.
Pottery production methods at San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán, an important center of this culture, reveal advanced techniques. Olmec potters mixed clay with sand from nearby rivers to improve its plasticity and malleability.
This meticulous process included stages of kneading and resting the clay to ensure a uniform consistency and to eliminate air bubbles, which was essential for the durability of the ceramic objects. Modeling was done entirely by hand, and river shells were possibly used to smooth and decorate the ceramic surfaces.
The focus of their pottery, both in its technical and symbolic aspects, underscores the importance of their pottery in the understanding of Olmec culture. Pottery not only served everyday purposes but also embodied essential aspects of Olmec identity and spirituality, leaving a lasting legacy that continues to fascinate researchers and admirers of this ancient civilization.
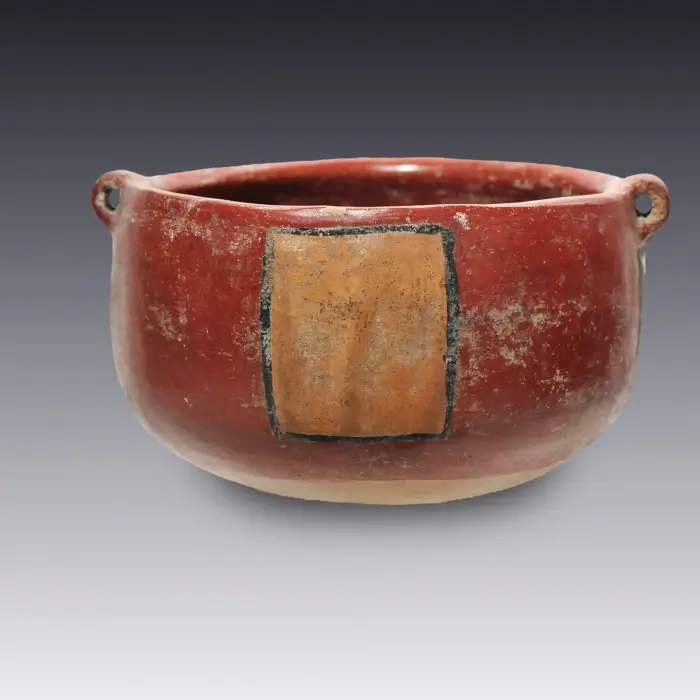

Functions and Uses of Olmec Ceramics
Olmec pottery, beyond its aesthetic value, played a fundamental role in the daily life and ritual practices of this ancient civilization. From imposing colossal heads to portable stone and ceramic sculptures, Olmec artistic production reflected both the mythological beliefs and social structure of the society.
These works not only represented authority figures with great naturalism, but were also used in the Mesoamerican ball game, evidencing their importance in social and religious activities.
The complex Olmec mythology, represented through their jade and ceramic artifacts, included a variety of characters and animal creatures, such as eagles and jaguars, which were believed to possess divine attributes. These representations were not only a means of documenting beliefs and myths, but also served as ritual ornaments, possibly worn by important leaders during ceremonies.
Later Mesoamerican cultures, such as the Maya and Aztecs, continued to venerate and use Olmec works, indicating the endurance and sacred value of these objects across generations. This exchange and reverence for Olmec objects underscores the transcendence of their ceramics, not only as art objects, but as central elements in the worldview and religious practice of the region.
Significant Archaeological Finds in the Olmec Culture
The Olmec culture, known for its advanced development in Mesoamerica, has been the subject of numerous archaeological discoveries that have provided a deeper understanding of their civilization. The iconic colossal stone heads, sculpted from basalt, are considered portraits of their rulers. These sculptures, which can reach almost 3 meters in height and weigh 8 tons, stand out for their unique facial features and the representation of protective helmets, possibly used in the Mesoamerican ball game or as symbols of political and religious power.
Findings at sites such as San Lorenzo and La Venta have revealed not only the magnitude of their monumental art, but also the complexity of their religious and ritual practices. La Venta, in particular, is famous for its Great Pyramid, a structure that stands as the largest building in Mesoamerica at that time. These sites have provided valuable information about the Olmec cosmovision, including the belief in a cosmos divided into three parts: the Underworld, Earth and Heaven.
The tradition of burying their sculptures, even the larger ones, could be interpreted as a ritual act of remembrance, pointing to the cultural and religious importance of these works. In addition, the discovery of offerings in places like El Manatí, including wooden sculptures, rubber balls and infant bones, suggests the practice of ritual sacrifices that were an integral part of their spirituality.
The impact of the Olmec extended beyond their ceremonial centers, influencing later civilizations in Mesoamerica. Deities represented in Olmec art, such as the Dragon God and the Feathered Serpent God, would reappear in later cultures, demonstrating the endurance of their spiritual and artistic legacy.
Influence of Olmec Art and Ceramics in Mesoamerica
Olmec pottery, renowned for its refinement and rich iconography, profoundly marked the artistic and cultural development of Mesoamerica. This influence was manifested not only in ceramic aesthetics and techniques but also in the adoption of religious and symbolic motifs by later cultures.
Olmec art and especially their ceramics not only demonstrate advanced artistic skill, but also reflect important aspects of their worldview, which were integrated by civilizations such as the Maya and Aztecs into their own religious and artistic practices.
The presence of Olmec artifacts in sites far from their geographic core is evidence of the extensive trade network and cultural influence of this pre-Columbian people in the region.
This Olmec legacy extended beyond their time, influencing the organization of ceremonial spaces, the construction of monumental pyramids and the performance of sacrificial rituals in Mesoamerica. Thus, all subsequent Mesoamerican cultures were indebted to the Olmecs, recognizing in them their mysterious precursors.
Therefore, Olmec pottery not only influenced the people who came later in the Mesoamerican area, but has been a reference and inspiration to contemporary potters around the world.
We hope you liked this post. It will help us if you share it on social networks





